When it comes to choosing the correct industrial seal types for your product, you should first answer a few key questions to avoid malfunctions. Depending on the application of a particular seal, the wrong choice of the seal may result in poor product performance, expensive defects, or even serious injury.
What is the purpose of the industrial seal? What temperature will the seal be exposed to? What chemicals will the seal be exposed to? What weather conditions can the seal work in? Does the seal have to meet any standards? The answers to these questions will help determine the correct seal type and required materials.
This guide will take you through the most common types of industrial seals that industrial designers and engineers consider when designing new products.
Sealing with Gaskets
A gasket is a custom-shaped rubber or other flexible material that is placed between two surfaces to seal the connection between them. The gasket can be made of silicone, neoprene, polyurethane, EPDM, or other materials. In order to form a reliable seal, it is even necessary to compress the surroundings.
When explaining the best material and design for a particular gasket, it is important to consider the environmental conditions in which the machine or product will be used. For example, silicone gaskets are waterproof and flexible, suitable for high and low temperatures, while the advantage of neoprene is that it can best create a permanent seal.
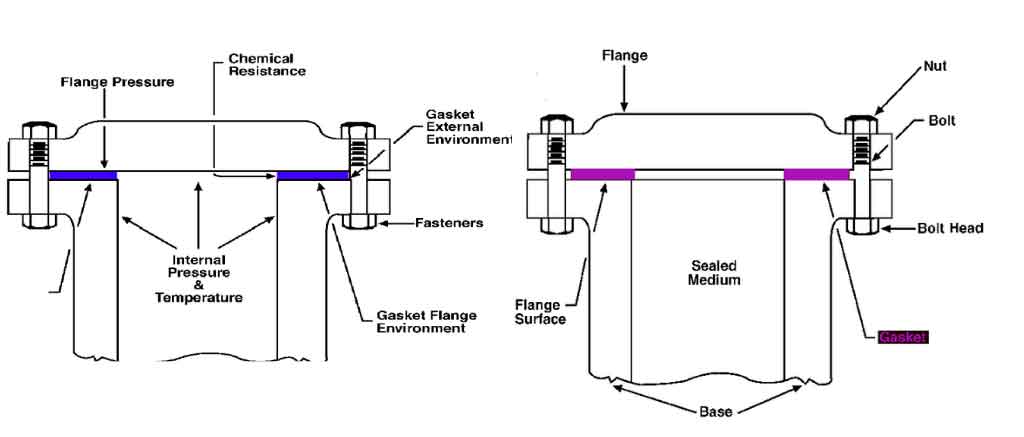
Types of Gasket
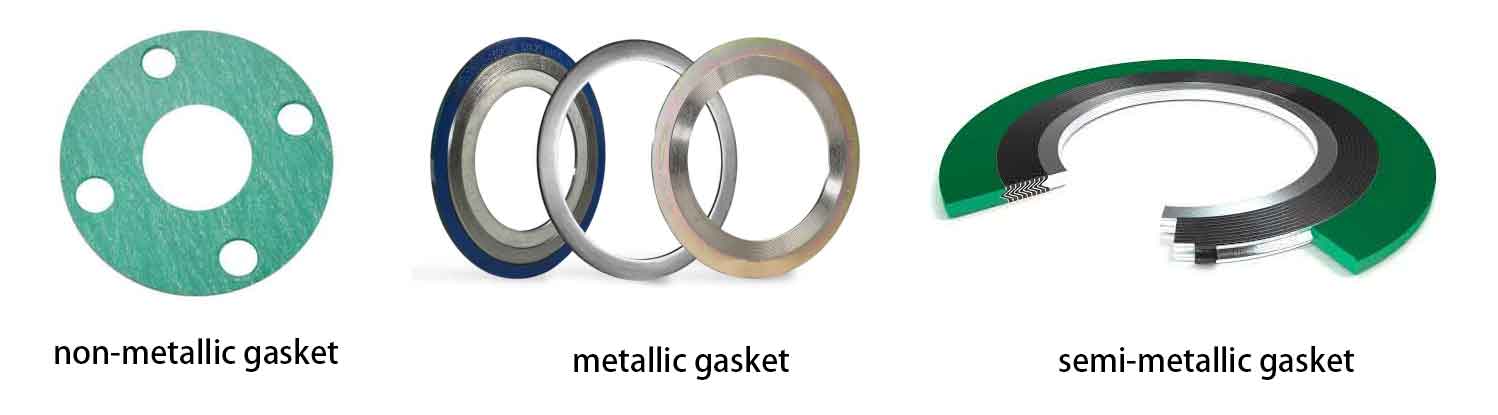
The gasket is one of the common types of industrial seals. It can be clearly divided into three types, including non-metallic, semi-metallic, and metallic gaskets.
Metal gasket
Metal gaskets consist of one or more metals and are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, pressures, and chemical exposure. Compared with non-metal gaskets, metal gaskets can be used for higher-quality surface sealing. These gaskets are very suitable for medium and high-pressure environments.
Semi-Metallic gasket
Semi-metal gaskets are made of a mixture of metal and non-metal materials. Metal can provide strength and elasticity, while non-metal parts provide consistency and sealing.
With a high temperature and pressure-resistant semi-metal design, semi-metal can be applied to almost all working conditions, such as convex, internal and external convex, tongue and groove flanges.
Non-metallic gasket
The non-metallic gasket is a material that is easy to compress under bolt load and has zero metal content. It can be selected from a variety of elastomers, compressed non-asbestos, polytetrafluoroethylene, flexible graphite, and high-temperature sheet products.
Since non-metallic gaskets can be purchased in many cut shapes, sheets, or rolls, non-metallic gaskets have been widely used in many applications, including pipe flanges, heat exchangers, compressors, and bonnet valves.
Sealing with O-rings
One of the most common types of industrial seals is an o-ring. O-rings can also be called packing or toroidal joints. The o-ring design is suitable for grooves on a surface to create a seal. Not only are they reliable and easy to install, but they are also very cheap. This makes them a good choice for static and dynamic applications.
There are a lot of materials that can be used for O-rings, and can be organized into two main categories include synthetic rubbers (thermosets) and thermoplastics. Two ways are available to fix the size of an O-ring size.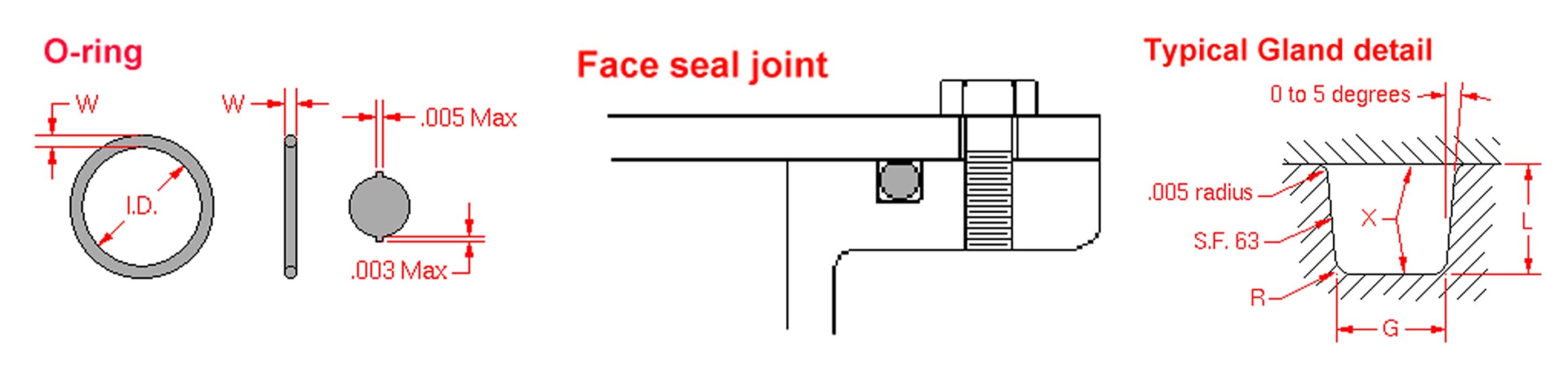
In the production process, the cord itself can be produced according to the required length or can be purchased in batches, and then cut and welded before use. The latter method, although sufficient for certain projects, is the less reliable of the two as the fused or glued cross-section becomes a weak point and may fail.
Types of O-rings
O-rings can be divided into flexible o-rings and liquid o-rings.
Flexible o-ring
The flexible o-ring can be hollow or solid, allowing compression and deformation. The force required to compress the o-ring can be customized by increasing or decreasing the wall thickness of the hollow o-ring. One advantage of using a flexible o-ring is that it will maintain its seal without the need for lubricants or adhesives. This type is most suitable for installation into a pre-existing groove without the need for a custom solid o-ring or molded seal.
Liquid rubber ring
Liquid o-ring is a synthetic lubricant and sealant. A common application is on pipe threads to ensure a waterproof seal. Liquid o-rings are suitable for internal and external threads to achieve smooth connection. Liquid o-rings also help seal damaged or corroded threads.
Interesting fact: The Challenger disaster in 1986 was determined to be caused by the failure of the O-ring. Extremely low temperature makes the o-ring lose its flexibility and become brittle. NASA later redesigned their joint design, using three o-rings instead of two, and an onboard heater. There have been no reports of o-ring problems since then!
O-rings Production
O-rings can be manufactured using a variety of processes: extrusion and pressure or transfer molding.
Extrusion is the creation of an object by passing it through a mold in its desired cross-sectional shape. For example, the cross-section of an O-ring will resemble an “O” shape. This will allow the production of a hollow tube piece. Extrusion can only be used when creating objects with a consistent cross-section because only the length of the object can be adjusted. This method is similar to the method of extruding Pelto from a plastic mold.
Pressure and transfer molding are the processes of forcing material into the mold cavity. Pressure forming involves turning off the heated material on the top of the mold so that it is in contact with all surfaces of the mold. Transfer molding, on the other hand, is a process in which the casting material is forced into a closed mold. Transfer molding allows higher dimensional tolerances and less environmental impact.
The seal adopts over-molded rubber seals
Another product sealing method is over-mold sealing. An over-molded seal is applied directly to the surface of water and dust. For example, the Samsung Galaxy S5 has an over-molded seal on the back to protect the battery and circuit from water damage.
In this case, compared with the use of o-rings, the advantage of over-molding is the ability to cast complex shapes on a flat surface. Putting the o-ring into such a complicated frame may risk slippage or loss of elasticity.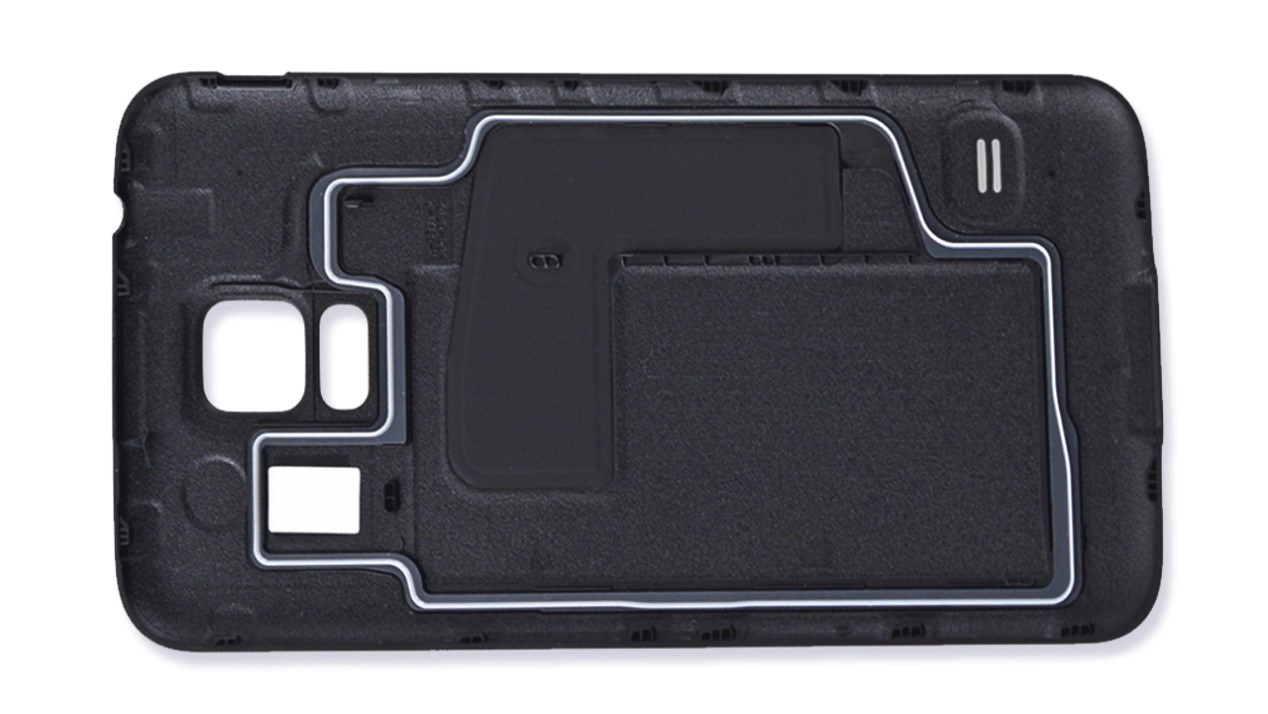
With proper information and comprehensive consideration of the environmental conditions your product will face, it is easy to choose the best waterproof or dustproof method for your production process. However, for commercial products, it is strongly recommended to seek professional advice. Need help choosing the best seal type or material for your product? Contact us and we will help guide your decision-making process.
Conclusion
Each industrial seal has its specific characteristics, and we should choose the right types according to your applications. Besides, some other seals can also be used to ensure the effective sealing of components, such as quad rings, square rings, lip seals, shaft seals, backup rings, and u-cups seals.
Therefore, the choice of the industrial seal must depend on the nature of the application, the area of use, and the expected application cycle. You can talk to the manufacturer about your requirements. He or she will suggest you the correct industrial seal, which performs very well in your application.




